1. Installing GemBuilder for Java
This Installation Guide describes how to install GemBuilder for Java (GBJ) into a GemStone Repository, and how to configure Java clients to log in to GemStone using GBJ.
This version of GemBuilder for Java supports both 32-bit GemStone/S, and GemStone/S 64 Bit 3.2.x and 3.3.x.
For details on the changes in this version of GBJ, see the GemBuilder for Java Release Notes for version 3.1.3.
The GemBuilder for Java installation process includes installing the GBJ interface files into the GemStone repository, and configuring your system to allow a GBJ Java application to log into GemStone. You need only install the GBJ interface files into the server once for each release of GBJ, but each Java client must be configured for login.
System Requirements
GemBuilder for Java includes components that are part of both the GemStone server and the Java client. A supported GemStone server product and version, and a supported client platform, are required
GemStone Server
Product and Platform
A supported GemStone object server version, installed on a network-accessible host.
GemBuilder for Java version 3.1.3 is compatible with 32-bit GemStone/S versions 6.7 and above, GemStone/S 64 Bit versions 3.2.15 and later 3.2.x versions, and 3.3.1 and above.
GemBuilder for Java v3.1.3 has been tested with the following server versions:
Supported platforms 
Supported platforms for the GemStone Server are provided in the Installation Guide for your server product and version.
Server keyfile
With versions of GemStone/S 64 Bit after v3.2 and GemBuilder for Java v3.1.3, authorization for using GemBuilder for Java is provided by the GS/64 keyfile. You will need to have a keyfile that provides authorization for use with GemBuilder for Java in order to use GemBuilder for Java. If you require a keyfile, write to keyfiles@gemtalksystems.com, or contact GemTalk Technical Support.
GemBuilder for Java Client
Supported Platforms
GemBuilder for Java clients are supported for the same set of platforms as the GemStone server that these clients will connect to. These platforms are provided in the Installation Guide for your server product and version.
You may run GBJ clients on supported platform other than the one your GemStone server is running on, provided you use the appropriate client libraries.
With GemStone/S 64 Bit, which does not support running the server on Windows, you may run GBJ clients on Windows by using the Gemstone/S 64 Bit Windows client distribution.
Note that since Oracle does not provide 32-bit versions of Java 1.8 on Solaris, GBJ 3.1.3 and later clients cannot be used on Solaris with 32-bit GemStone/S servers.
Server Shared Libraries
GBJ clients must have access to shared libraries that are linked for a specific version of GBJ and a specific version of the GemStone server. These shared libraries are distributed with the GemStone server with GemStone/S 64 Bit.
Each GemStone/S 64 Bit distribution includes the GBJ shared libraries for the most recent previous GBJ version. For a GBJ release such as this that does not coincide with the GemStone server release, please contact GemTalk Technical Support for the correct libraries for your server version/s and platform/s.
Installing GemBuilder for Java into the GemStone Server
The following instructions describe installing the GemBuilder for Java Smalltalk code into your GemStone/S or GemStone/S 64 Bit repository. Once the GemBuilder for Java code is installed, you will configure your client machines to log in to this repository.
If you are upgrading from an older version of GemBuilder for Java, follow this process to install version 3.1.3.
Note that if you are upgrading from a GBJ 2.x version, the GBJ 3.x class names are different; both the 2.x and 3.x versions of GBJ will be available after this installation process. Carefully review the GBJ 3.0 Release Notes , as well as the Release Notes for all intermediate versions, to determine how the changes affect your application.
Prepare for Installation
1. Select an installation directory, installdir, and make this directory the current working directory.
You can install GemBuilder for Java in any directory. We recommend installing GBJ at the same level as the GemStone server installation directory. You will need about 6 MB of free disk space.
2. GemBuilder for Java is provided as a zipped archive file, GemBuilderJava3.1.3.zip. Move this distribution file to the directory location in which GemBuilder for Java will be installed.
3. Unzip the distribution file using unzip.
InstallDir now contains a GemStone directory with a name similar to GemBuilderJava3.1.3. In the instructions that follow, we refer to this directory as gbj_directory.
gbj_directory includes the following:
version.txt
README.txt
PACKING.txt - list of file contents
gbj313.jar - the Java class library
gbjopensrc313.jar - class library with open source libraries used by the GBJ tools
GbjTest.zip - example Android application
README.android.txt - readme for Android application
doc - directory containing GemBuilder for Java javadocs documentation:
index.html - the entry point for the online javadocs documentation
api - directory containing support files for the online javadocs documentation.
copyinfo.html - intellectual property ownership information
open_source_licenses.txt - licenses for open-source components.
sources.html - Further information and GemStone Technical Support
server - directory containing:
GbjFileinReader.gs
GbjGciForwarder.gs
GbjGciInterface.gs
GbjHypericServerTemplate.xml
GbjHypericServiceTemplate.xml
GbjJmxCommandsTemplate.dat
GbjJmxSystemStatsTemplate.dat
GbjToolsInterface32.gs
GbjToolsInterface.gs
install32.gs
install.gs
Environment Setup
GemBuilder for Java version 3.1.3 requires several environment variables to be set prior to installation, including the path.
1. The GEMSTONE environment variable, $GEMSTONE or %GEMSTONE%, should be set to the GemStone server installation directory. This is described in the GemStone server documentation. Verify that this is set correctly.
2. Your path should include the path for the Gemstone Server executables,
$GEMSTONE/bin or %GEMSTONE%\bin.
3. $GBJ or %GBJ% should be set to the GemBuilder for Java installation directory.
% setenv GBJ gbj_directory
$ GBJ=gbj_directory
$ export GBJ
On Windows, you may set this using the System control panel, or execute the following:
c:\> set GBJ=gbj_directory
Installing GemBuilder for Java into your Repository
1. If necessary, start up the GemStone repository monitor (Stone). You may also want to start a NetLDI for use later in testing the GBJ installation.
2. At a command prompt, cd to a working directory, in which you want the installation log to be created. You must have write permission for this directory.
3. Log in to the GemStone server as SystemUser, using linked Topaz. Use the -i switch, which keeps Topaz from reading any initialization file you might have.
4. File in the server component, which is located in the server directory of the GemBuilder for Java installation tree.
If you are installing into GemStone/S 64 Bit, use the file install.gs; if you are installing into 32-bit GemStone/S, file in install32.gs.
topaz 1> input $GBJ/server/install.gs
During the file-in operation, output is directed to the file Gbj313ServerFilein.log in the current directory.
The file-in operation should end with a message that the errorcount is 0. If errorcount is not 0, errors have occurred; contact GemStone Technical Support, providing the file Gbj313ServerFilein.log as well as details about the installation process.
The installation script performs the commit, so you do not need to commit.
topaz 1> quit
Your GemStone server is now ready for use by GemBuilder for Java clients.
Client Setup
Preliminaries
Verify that TCP/IP networking is functional on your client machine, and that there is a network path to the Stone’s host. You will need to have the Stone and a NetLDI running, and the GBJ server component should have been successfully installed in the Stone.
Copy GBJ files to the client
If you are running the GBJ client on the same machine as the GemStone server, you can set your GEMSTONE, CLASSPATH and PATH or LD_LIBRARY_PATH to existing GBJ and server installation directories. However, if you are running the GBJ client on a separate machine, you will need to set up the client machine with the correct files.
1. GBJ jar files
If you are running the GBJ client on the same machine as the server, use the existing location configured in $GBJ.
If the GBJ client is on a different machine, install the GBJ distribution on the client. You may install these from the distribution archive as was done on the server, as described under Prepare for Installation. You may also copy the required files from the server installation.
The required files from the GBJ distribution are the jar file gbj313.jar and, if you are using the GBJ development tools, gbjopensrc313.jar. However, the javadocs provide key documentation for GBJ functions and should also be copied to the client.
The directory containing the GBJ jar files accessible to the client will be referred to as gbj_jar_dir.
2. GBJ and GCI client shared libraries
The GBJ clients require access to both the GCI (GemStone server) shared libraries and the GBJ shared libraries. All these shared libraries are specific to the server product and version and to the client platform; the GBJ shared libraries are also specific to the version of GBJ.
If you are running the GBJ client from a machine other than the GemStone server machine, copy the GCI client libraries to a location accessible from the client machine. If this is a different platform than the one the GemStone server is running on, you may need to use the GemStone server distribution for a platform other than your server platform to locate the correct libraries. Contact GemStone Technical Support if you cannot locate the correct client libraries.
The client libraries are located in the directory $GEMSTONE/lib on UNIX or Linux, or %GEMSTONE%\bin on Windows.
There are also linked versions of the GCI client libraries, which you may use in custom GBJ applications. The GBJ tools support only RPC logins.
Note that only 64-bit applications are supported with GBJ with GemStone/S 64 Bit, and only 32-bit application with GBJ with 32-bit GemStone/S. Libraries are provided for 32-bit java applications for GemStone/S 64, for convenience, but these have not been certified.
The server shared libraries may be located in any directory on your library load path, with the exception of the GCI library for GemStone/S 64 Bit Windows clients. For GemStone/S 64 Bit clients on Windows, you should copy the libgcirpc-NNN-64.dll library to the %GEMSTONE%/lib directory.
The following table lists the names of the required shared library files, including both the GBJ shared libraries and the GCI shared libraries.
The directory containing the server GBJ and GCI shared library files will be referred to as shared_library_dir.
Set environment variables
2. GBJ_GSVERSION
Set the GBJ_GSVERSION environment variable to the GemStone server version. For example (UNIX or Linux, using bash shell):
This environment variable is not required if you have a complete GemStone installation; GBJ can also read the version number from $GEMSTONE/version.txt. or %GEMSTONE%\version.txt.
3. CLASSPATH
The CLASSPATH environment variable must include the GBJ class library, gbj313.jar, and (if you are using the GBJ Tools) the open source library gbjopensrc313.jar. These must be in a directory accessible from the client, as described above in GBJ jar files. F
For example, to set the CLASSPATH on UNIX or Linux using bash shell:
$ export CLASSPATH=$JDK/lib:gbj_jar_dir/gbj313.jar:gbj_jar_dir/gbjopensrc313.jar
On Windows, you may set this using the System control panel, or execute the following:
c:> set CLASSPATH=%JDK%\lib;gbj_jar_dir\gbj313.jar;gbj_jar_dir\gbjopensrc313.jar
4. Shared Library Path
Set the shared library path environment variable to include the client library directory, shared_library_dir, as described above in GBJ and GCI client shared libraries.
On UNIX and Linux, the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable must include the directories containing the GCI and GBJ shared libraries. For example, using bash:
$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=shared_library_dir
On Windows, the %PATH% environment variable must include the directories containing the GCI and GBJ shared libraries. You may set this using the System control panel, or execute the following:
c:> set PATH=%PATH%;shared_library_dir
5. Executable path
If you have not already done so, add the Java executable directory to the path. To use the GBJ tools, you must have the Java executable directory, such as the JDK bin directory, on your path.
To set this on UNIX or Linux, for example, using bash:
$ export PATH=$JDK/bin:$PATH
On Windows, you may set this using the System control panel, or execute the following:
c:\> set PATH=%PATH%;C:\jdk1.8.0_102\bin
Start up the GBJ Launcher and log into GemStone
The GBJ Launcher allows you to specify the name and location of the GemStone server and the other parameters that control the login. Note that to log in to GemStone, you must have the GemStone server and a NetLDI running on the GemStone server machine, and be otherwise configured to allow login.
1. Invoke the GBJ Tools Launcher.
The GBJ Launcher is in com.gemstone.tools.GbjLauncher.This tool supports the following options on the command line:
- help — print a help message (to standard output)
- version — print GBJ version information
- UseLogFile filename — write log output to the specified file
- NoFileLogger — send log output to standard output rather than to a file
- UsePrefFile filename — use the specified file for the preferences file
- NoPrefFile — do not load or save a preferences file
To open the Launcher, with GemStone/S 64 Bit:
prompt> java -d64 com.gemstone.tools.GbjLauncher [options]
prompt> java com.gemstone.tools.GbjLauncher [options]
This opens the GBJ Tools Launcher
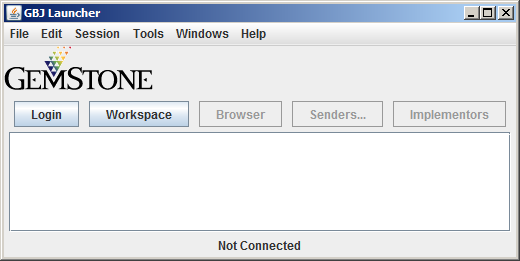
2. Enter Login Parameters
In the Tools Launcher, click Login to begin a session. A Session Parameters Dialog appears, prompting you for the session parameters.
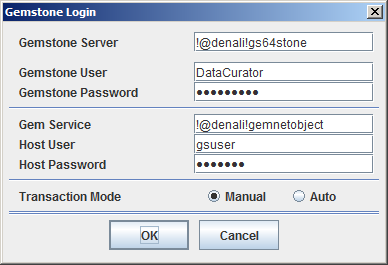
Fill in the session parameters, as described in Table 2 . More detail on the specific details for configuring login parameters can be found in the GemStone/S System Administration Guide.
3. Click Ok to log in
When the session parameters are correct, click Ok.
A successful login results in the event being recorded in the Launcher’s Text Pane, which serves as a transcript. Additional buttons are activated, and the Login button becomes Logout.
After you have successfully logged in to the GemStone server, you have verified that your GemBuilder installation is correct.
If the login attempt did not complete or if login fails, the console will contain log messages with java error details.
If this is not sufficient to determine the problem, you can configure more complete error messages by setting full logging. To do this, execute:
prompt> java com.gemstone.gbjgci.GbjGciPreferences set GBJ.LogLevel ALL
On Windows, running with Administrator privileges may be needed to allow registry update.
For more information on login parameters and on using the GBJ tools available from the GBJ Launcher, see the GemBuilder for Java Programming Guide and the GemBuilder for Java Tools Guide.